A low residue diet (LRD) is often prescribed for individuals with digestive issues or those recovering from surgery. It focuses on easy-to-digest foods that reduce the bulk of stool, minimize irritation in the intestines, and help people feel more comfortable during their recovery or flare-up of digestive conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or diverticulitis. If you’re following this dietary regimen, you may be wondering: Can you eat tuna on a low residue diet?
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore whether tuna can fit into a low residue diet, how to prepare it to maximize its digestibility, and how it provides valuable nutrients for those who need to manage their gut health. So, let’s get started!
What is a Low Residue Diet?
A low residue diet is designed to reduce the amount of undigested food that remains in your digestive tract. By limiting fiber and certain other hard-to-digest foods, this diet helps ease the burden on your intestines. It’s especially beneficial for people suffering from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Crohn’s disease, or those recovering from gastrointestinal surgeries.

This diet focuses on foods that are easy to digest, and typically requires the avoidance of high-fiber foods, such as raw vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes. By eating foods with low fiber content, the body can focus on healing without the added stress of processing complex, bulky food.
Nutritional Value of Tuna – Why It’s A Superfood For Your Health!
Tuna is a widely popular fish known for its health benefits and versatility. It’s available in several forms: fresh, frozen, and canned. Regardless of the form, tuna is an excellent source of protein, vitamins, and essential fats, making it a popular food choice for those on many different types of diets.
Key Nutrients in Tuna:
- Protein: Tuna is a high-quality, lean protein source that is rich in essential amino acids. Protein is vital for muscle repair and general body function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Tuna is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, which promote heart health and help reduce inflammation in the body.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Tuna is also packed with vitamins like B12, niacin (B3), and minerals such as selenium, phosphorus, and iodine.
These qualities make tuna an attractive option for many who are looking for a nutrient-dense, easy-to-digest protein source. But is it suitable for those following a low residue diet? Let’s take a closer look.
Read: When Nuclear Stress Testing Becomes Essential for Diagnosing Heart Problems
Is Tuna Safe On A Low Residue Diet?
The answer is yes, tuna can be safely included in a low residue diet. Here’s why:
- Low in Fiber: Tuna is a low-fiber food, which means it doesn’t contribute to excess stool bulk. This makes it an ideal protein choice for individuals with digestive issues.
- Easily Digestible: Tuna is soft, light, and easy on the digestive system. Whether canned or fresh, it doesn’t require much work for your body to process.
- Lean Protein: Tuna is a lean protein, which means it doesn’t have the heavy fats or oils found in other meats, making it easier to digest.
However, as with any food on a low residue diet, preparation matters. Certain forms of tuna, such as those packed in heavy oils or fried, may not be as easy on the stomach. For the best results, you should focus on canned tuna in water, or fresh tuna that’s grilled or baked without heavy seasonings or spices.
Best Types Of Tuna For A Low Residue Diet – Top Picks For Easy Digestion!
When following a low residue diet (LRD), it’s crucial to choose foods that are easy to digest and gentle on the digestive system. Tuna, being a lean and nutritious protein source, can be a great addition to your low residue meals. However, not all types of tuna are created equal when it comes to digestibility.
Canned Tuna in Water:
Canned tuna in water is one of the best options for a low residue diet. It is low in fat and doesn’t contain the heavy oils or preservatives that could potentially irritate the intestines. Additionally, it’s soft and easy to digest, making it perfect for individuals who need to follow a gentle diet.
Fresh Tuna (Grilled or Baked):
Fresh tuna is another great choice when prepared simply. Grilled or baked fresh tuna without heavy seasoning is a lean protein that’s both nutritious and easy to digest. Fresh tuna retains its high-quality nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, and is gentle on the stomach as long as it’s not fried or heavily spiced.
Tuna in Pouch (Packed in Water):
Tuna that comes in pouches and is packed in water is a convenient and easily digestible option. It’s similar to canned tuna in water but comes in a lightweight, resealable pouch. This option can be just as low in fat and free from the high oil content that could make it hard to digest.
Avoid Tuna in Oil or Fried Tuna:
Tuna packed in oil or fried tuna should be avoided when following a low residue diet. The oil or the frying process increases the fat content, making the tuna harder to digest. Higher fat content can irritate the digestive system and may contribute to bloating or discomfort, especially for those with sensitive digestive tracts..
How To Prepare Tuna On A Low Residue Diet?
Preparation is key when it comes to tuna and a low residue diet. Here are some of the most digestible ways to prepare tuna:
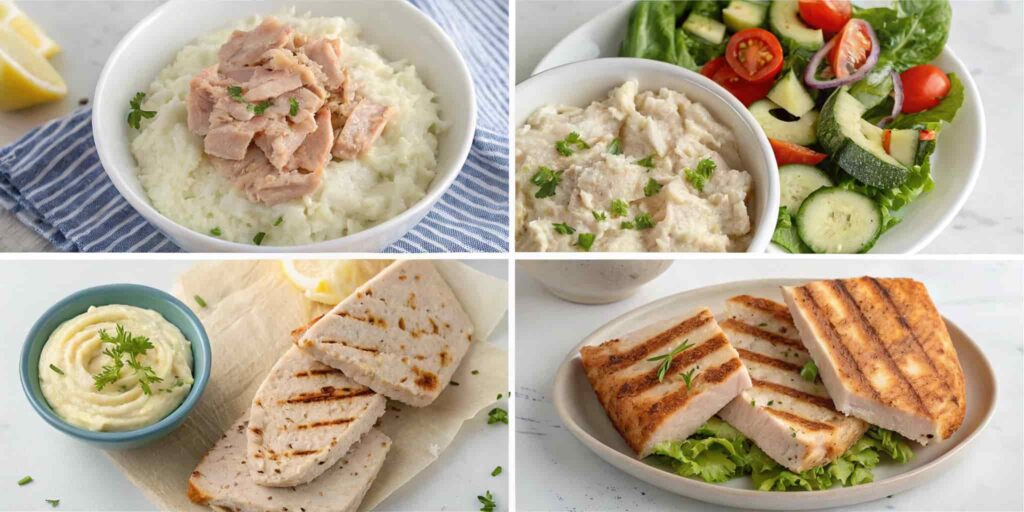

- Plain Canned Tuna: For the simplest preparation, open a can of tuna packed in water, drain it, and mix it with a small amount of mayonnaise. This quick and easy method is light on the stomach and low in fiber, making it perfect for a low residue diet.
- Tuna with Soft Foods: Pairing tuna with soft, low-fiber foods like mashed potatoes, white rice, or scrambled eggs makes for an easy-to-digest meal. These foods don’t add excess fiber and blend well with tuna for a gentle meal.
- Grilled or Baked Fresh Tuna: Grill or bake fresh tuna without heavy spices or oils to keep it simple and digestible. Light seasoning with salt, pepper, or lemon is acceptable, but avoid strong spices or frying, as they can irritate the digestive system.
- Tuna Salad (Low Residue Style): To make a low residue tuna salad, mix canned tuna with mayonnaise or a mild dressing and avoid high-fiber ingredients like raw vegetables. Stick to soft bread like white bread instead of whole grains for a lighter and more digestive-friendly option.
- Tuna on White Bread: For a low-residue tuna sandwich, spread the drained tuna mixed with mayonnaise on soft white bread. White bread is low in fiber, making it a suitable option for those following a low residue diet.
- Tuna with Scrambled Eggs: Scramble a couple of eggs in a pan with a bit of butter or oil, then mix in drained tuna for a protein-rich breakfast or lunch. This combination is easy on the digestive system and provides a good balance of protein and fat without the added fiber.
Tuna Recipes for Low Residue Diets – Simple, Tasty, And Gut-Friendly!
If you’re looking for meal ideas, here are some simple recipes that feature tuna and are perfect for a low residue diet:
Tuna with Mashed Potatoes:
Ingredients:
- 1 can of tuna (in water)
- 1 cup of mashed potatoes (prepared without skins or spices)
Instructions:
- Drain the canned tuna and mix it with mashed potatoes.
- Add a small amount of butter or cream for extra flavor.
- Serve warm as a simple, easy-to-digest meal.
Tuna on White Bread:
Ingredients:
- 1 can of tuna (in water)
- 2 slices of white bread
- Mayonnaise
Instructions:
- Drain the tuna and mix it with mayonnaise.
- Spread the mixture onto two slices of white bread.
- Enjoy a light, low-residue tuna sandwich.
Tuna with Scrambled Eggs:
Ingredients:
- 1 can of tuna (in water)
- 2 eggs
- Butter or oil for scrambling
Instructions:
- Scramble the eggs in a pan with a small amount of butter or oil.
- Add the drained tuna to the scrambled eggs.
- Stir well and serve for a protein-packed breakfast or lunch.
These recipes are simple, easy to digest, and perfect for anyone following a low residue diet.
Read: Dealing with Dizziness: Why It’s So Common in Chronic Pain Sufferers
Nutritional Benefits of Tuna – What Makes It A Super Healthy Choice?
Tuna offers several nutritional benefits, making it an excellent choice for those on a low residue diet. Here’s a breakdown of the key nutrients it provides:
- High-Quality Protein: Tuna is a lean protein that helps maintain muscle mass, support metabolism, and repair tissue. This is particularly important for those on restricted diets, as maintaining protein intake can be challenging.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The omega-3 fatty acids in tuna support heart health, reduce inflammation, and promote cognitive function. These essential fats are beneficial for overall health, especially for those with inflammatory conditions.
- Rich in B Vitamins: Tuna is rich in B vitamins, particularly B12, which supports energy production, nerve health, and overall vitality.
- Minerals: Tuna is also a good source of minerals like selenium, phosphorus, and iodine, which play key roles in supporting immune health, maintaining bone structure, and regulating thyroid function.
- Low in Calories and Fat: Tuna is low in calories and fat, making it an ideal choice for those who are looking to maintain a healthy weight or reduce their fat intake. The low-fat nature of tuna helps ensure that it remains easy to digest while providing essential nutrients without excess calories.
What Foods Should You Avoid On A Low Residue Diet?
When following a low residue diet, it’s essential to avoid foods that are high in fiber or difficult to digest, as they can irritate the digestive system and increase stool bulk. These include whole grains like brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread, which are rich in fiber and can cause discomfort. Raw vegetables, such as leafy greens, carrots, and broccoli, should also be avoided because they contain hard-to-digest cellulose.
Legumes like beans, lentils, and chickpeas, which are high in fiber and can lead to gas or bloating, should be excluded from your diet. Additionally, nuts and seeds, although nutritious, are high in fiber and can be challenging for the intestines to process. Spicy, heavily seasoned foods, and fried or greasy foods should also be limited, as they can irritate the digestive tract and lead to discomfort or flare-ups.
Read: What You Should Know Before Your First Doctor’s Appointment
Low Residue Protein Alternatives – Dont Miss Out!
If you’re looking for variety in your protein sources, here are some other low residue protein options:
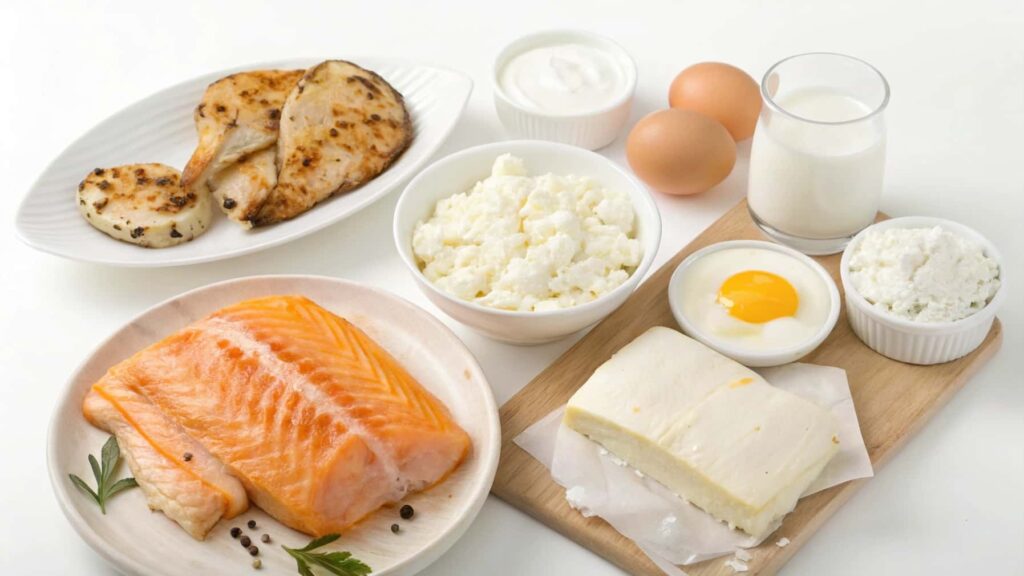

- Skinless Chicken: Baked or boiled skinless chicken is an easy-to-digest source of protein.
- Eggs: Scrambled, poached, or boiled eggs are soft and easy on the digestive system.
- White Fish: Fish like cod, tilapia, and haddock are gentle on the stomach.
- Silken Tofu: This is a soft protein source that can be incorporated into smoothies or soups.
- Low-fat Dairy: Yogurt and cheese (in moderation) are good alternatives for protein and calcium.
FAQs:
Can I eat tuna salad on a low residue diet?
Yes, you can enjoy tuna salad, but make sure to stick to low-fiber ingredients. Use mayonnaise or a mild dressing and avoid raw vegetables like onions, celery, or peppers. White bread or soft crackers can be used instead of whole grains.
Is canned tuna a good source of protein?
Yes, canned tuna is a fantastic source of lean, high-quality protein. It helps maintain muscle mass and supports tissue repair. It’s also a convenient and easy-to-digest protein option for those following a low residue diet.
What foods should be avoided on a low residue diet?
You should avoid high-fiber foods like whole grains, raw vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Spicy, heavily seasoned, or fried foods should also be excluded, as they can irritate the digestive system. Focus on soft, easy-to-digest foods that are gentle on your intestines.
Can I have tuna on white bread?
Yes, tuna on white bread is a good option for a low residue diet. White bread is low in fiber and easy to digest, making it an ideal pairing with tuna. Just be sure to use soft bread and avoid whole grain varieties.
What are the health benefits of tuna?
Tuna is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health and reduce inflammation. It’s also high in B vitamins, particularly B12, which helps with energy production and nerve health. Tuna provides high-quality protein, which is essential for muscle maintenance and overall bodily functions.
Can I eat tuna with mashed potatoes?
Yes, pairing tuna with mashed potatoes is a great choice for a low residue diet. Mashed potatoes are soft and easy to digest, making them an ideal companion to tuna. This combination provides a well-balanced and gentle meal for the digestive system.
Final Thoughts:
In conclusion, tuna is a great choice for those on a low residue diet. It’s a lean, nutrient-dense protein that is easy to digest, providing numerous health benefits without straining the digestive system. By selecting the right types of tuna and preparing it properly, you can enjoy this healthy food as part of your low residue meal plan.
Whether you’re eating it plain, in a salad, or paired with soft foods like mashed potatoes or white rice, tuna offers variety and convenience for those seeking easy-to-digest meal options. Always consult your healthcare provider or dietitian to ensure the low residue diet is tailored to your needs and that you’re meeting your nutritional requirements.
Also Read:

Leave a Reply