Salpingectomy, or fallopian tube removal, removes one or both fallopian tubes through surgery. Doctors may recommend this procedure to treat specific medical conditions or as a preventive measure. It helps address various health issues and offers potential long-term wellness benefits. Learn why doctors perform fallopian tube removal, the surgical techniques they use, the recovery process, and its impact on fertility.
Reasons for Fallopian Tube Removal
The fallopian tubes play a role in reproduction, but certain medical conditions may require their removal to protect a person’s health. From emergencies to preventative care, doctors use salpingectomy to address various serious concerns. Here are three key reasons why doctors recommend this procedure:
Ectopic Pregnancies
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube. This condition creates significant health risks, including tube rupture and internal bleeding. Doctors often remove the affected fallopian tube to prevent life-threatening complications.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease causes severe inflammation and scarring in the fallopian tubes. This damage leads to chronic pain and infertility. In severe cases, doctors remove the damaged tubes to relieve symptoms and stop recurring infections.
Cancer Prevention
Doctors increasingly perform salpingectomy as a preventative measure for high-risk individuals. Since many ovarian cancers begin in the fallopian tubes, removing the tubes significantly lowers the risk of these cancers. This approach is especially common for individuals with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer.
Surgical Procedures for Tube Removal
If you’re looking into surgery for fallopian tube removal, here’s a quick overview of the methods and how to prepare:
- Laparoscopy: Surgeons perform this minimally invasive procedure by inserting a small camera and specialized tools through tiny incisions in the abdomen. This method shortens recovery time, minimizes scarring, and reduces the risk of infection.
- Laparotomy: Surgeons use this open surgery technique to make a larger abdominal incision and access the fallopian tubes. They typically choose this method for complex cases involving significant scarring or tissue damage. Although recovery takes longer, it works well for certain medical conditions.
- Preparation: Patients undergo preoperative evaluations, such as blood tests and imaging studies, to make sure the procedure meets their unique medical needs.
Recovery Process
After the procedure, patients might feel abdominal pain, which doctors usually manage with prescribed medications. Patients may also experience common symptoms, such as nausea and fatigue, during the initial recovery period. At home, patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and excessive physical exertion. They should eat a healthy diet and stay hydrated to promote healing and lower the risk of complications. Attending follow-up appointments enables healthcare providers to monitor recovery, assess progress, and address any concerns or issues that may arise.
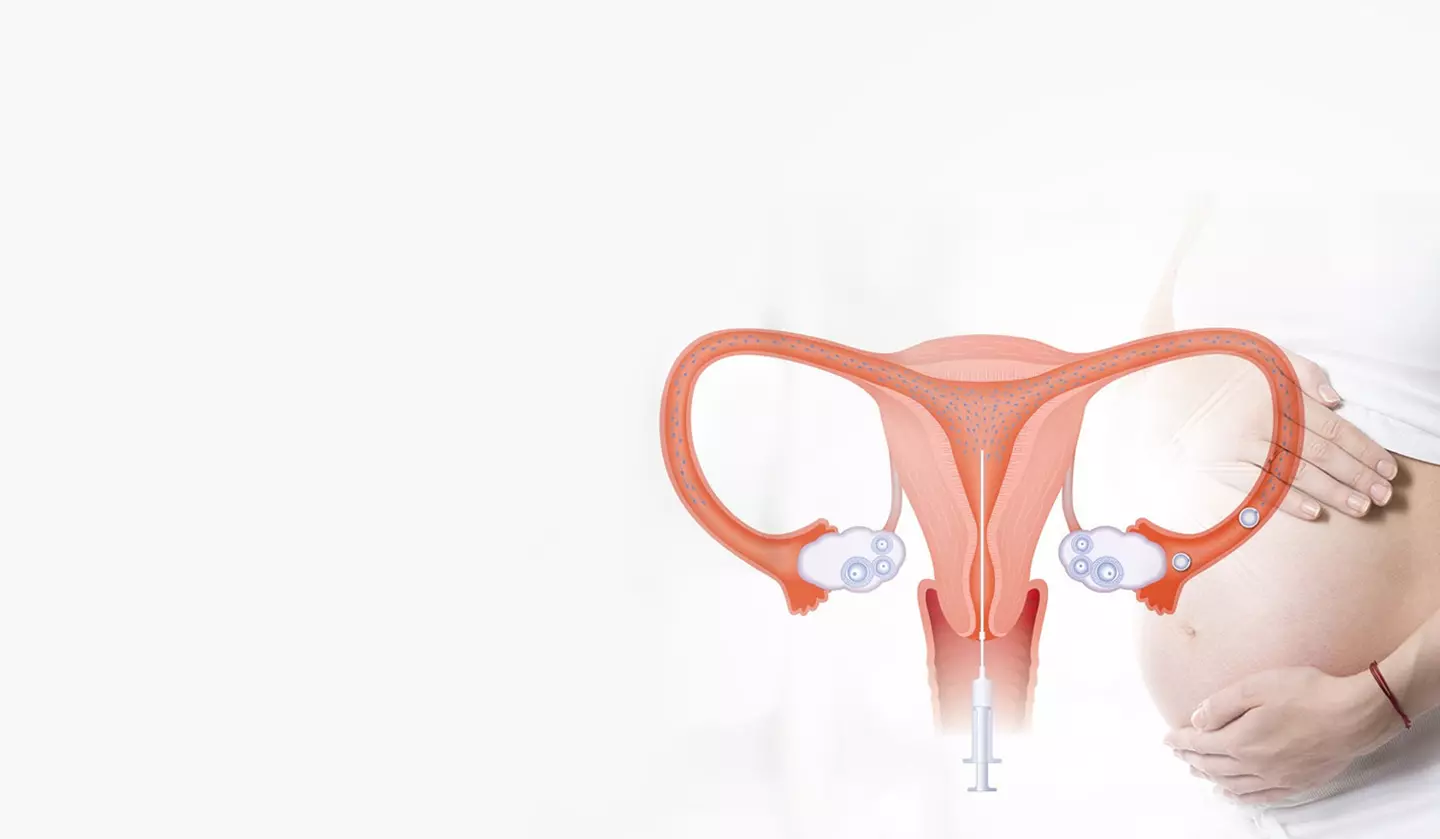
Impact on Fertility
Removing one or both fallopian tubes can reduce or eliminate natural conception, depending on the procedure. If one tube remains, natural conception may still be possible, but less likely. For those pursuing parenthood after tube removal, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is a viable option, bypassing the tubes entirely. Consulting a fertility specialist is recommended to explore options and receive personalized guidance.
Consult a Healthcare Provider Today
Fallopian tube removal is a medically significant procedure with a range of applications, from addressing ectopic pregnancies to preventing cancer. By understanding the reasons, surgical approaches, recovery processes, and fertility implications, individuals can make informed decisions about their health. For more personalized advice or to explore your options further, schedule a consultation with a qualified healthcare provider today.
- How To Improve Gut Health – Boost Digestion, Energy & Immunity!
- Is Coffee Beneficial To Health – Expert Insights You Can’t Afford To Miss!
- TimesHealthMage Diet Plans For Diabetics – Manage Blood Sugar The Smart Way!
- Which Type Of Exercise Is Best For Improving Cardiorespiratory Fitness – Expert Advice!
- Fitness Ryldoria Vornik – A New Way To Feel Strong!

Leave a Reply