An ankle fracture refers to a break in one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint. This type of injury is common and can impact daily activities, mobility, and overall physical health. Understanding the stages of healing after an ankle fracture is beneficial for anyone managing recovery, whether the injury is minor or involves more complex damage. Here is more information on this type of fracture, the causes, symptoms, treatment methods, and what to expect during recovery:
What Is an Ankle Fracture?
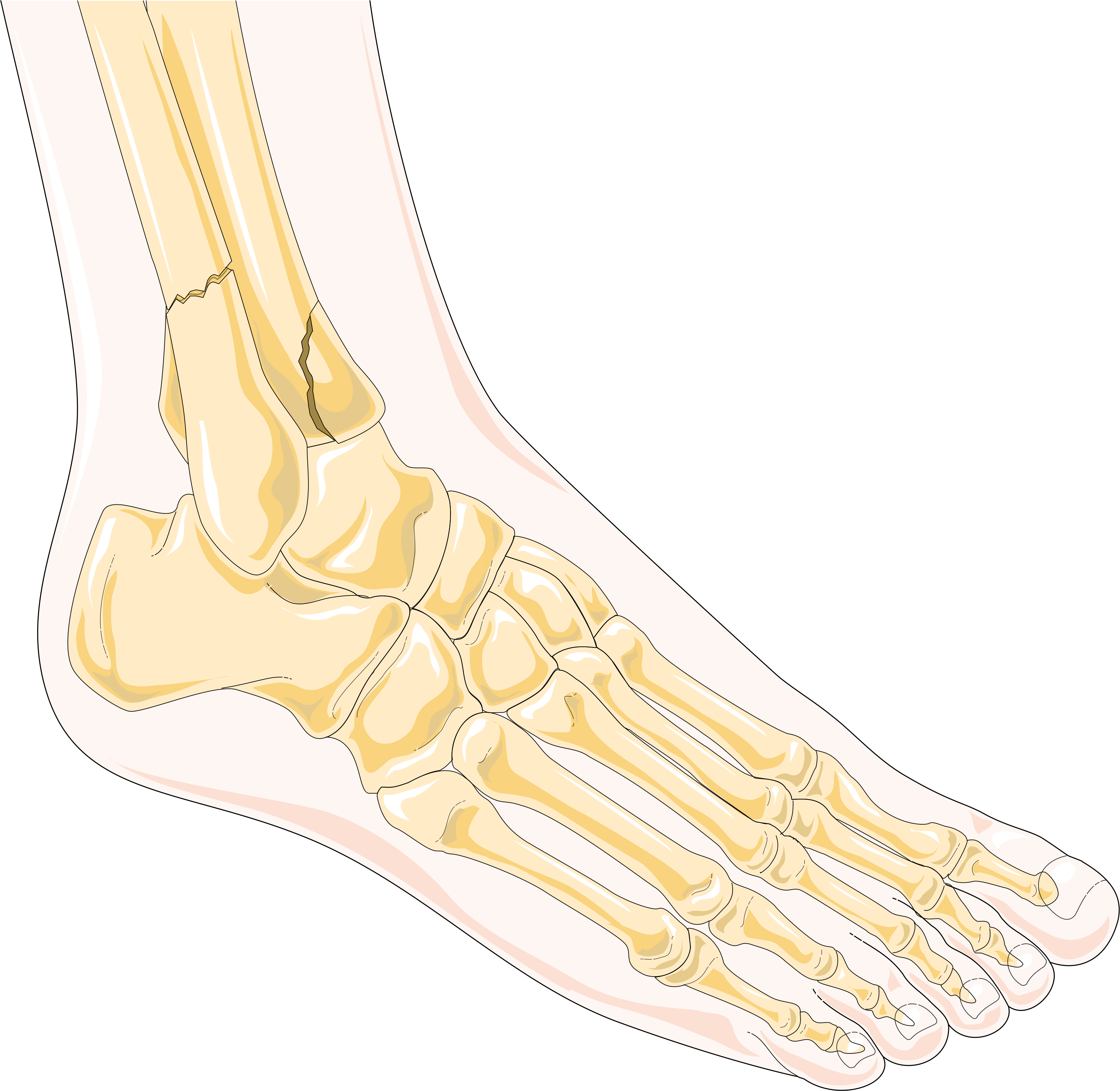
An ankle fracture occurs when there is a break in the bones forming the ankle joint. The main bones involved include the tibia (shinbone), fibula (the smaller bone of the lower leg), and talus (the bone that sits between the heel bone and the tibia and fibula). Fractures can range from a small, simple crack to multiple breaks involving several bones. The severity of the fracture helps determine the treatment plan and the recovery timeline.
Medical professionals often classify ankle fractures according to the location and number of bones affected. Stable fractures may involve a single break and minimal change in the position of the bones. Unstable fractures can involve multiple bones, joint dislocation, and require a more complex treatment approach.
What Are the Causes and Symptoms?
Most fractures occur due to acute trauma. Common causes include falls, twisting injuries, sports accidents, or direct impacts such as those experienced during car accidents. Osteoporosis and other bone-weakening disorders can increase the risk of sustaining a fracture even after minor incidents.
Symptoms of an ankle fracture usually develop immediately after the injury. Common signs include intense pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg. Deformity and visible changes in alignment can indicate more severe fractures. Loss of mobility or presence of numbness may also occur if nerves or blood vessels are involved.
How Is a Fracture Treated?
Treatment for an ankle fracture depends on several factors, such as the location, type, and severity of the injury. Medical evaluation typically begins with a physical exam and imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to assess the extent of the fracture. Minor fractures often respond well to immobilization using a cast or brace, which keeps the bones in proper alignment during the healing phase. Surgical intervention may be needed for more complex or unstable fractures.
What Can You Expect During Recovery?
Recovery from a fracture involves several distinct stages. The initial focus is on protecting the injured area to enable bone healing. During this time, weight-bearing is often restricted, and assistive devices such as crutches may be recommended. Pain management and control of inflammation play a central role during the early phase.
Once the fracture begins to heal, gradual introduction of movement and physical therapy are implemented to restore flexibility and strength. Swelling and mild discomfort may persist as tissues adapt. Progress varies based on the nature of the fracture and the type of treatment received.
Some individuals may return to normal activities within weeks, while severe fractures can require a longer recovery. Adherence to follow-up visits with healthcare providers supports appropriate monitoring of bone healing. Repeat X-rays and physical examinations help guide decisions about when to advance physical activity or remove immobilization devices.
Facilitate Your Healing Process
Understanding the stages of healing after an ankle fracture supports a smoother recovery. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, available treatments, and recovery expectations allows individuals to participate in their care more effectively. For personalized advice or questions about recovery, contact your healthcare provider for professional guidance.
- Zirconia Cap Price: Estimated Cost & Its Long-Term Benefits
- FREHF – The Revolutionary Future Of Human-Centered Technology!
- Adsy.Pw/Hb3 – Boost Your SEO And Drive More Traffic!
- Fitness Based Vacations By Timeshealthmage.com!
- TimesHealthMag Tips For Improving Sleep Quality – Expert Advice For Better Rest!

Leave a Reply